How many types of 3D printers are there?
In the world of 3D printing, understanding the various types of printers available is vital before entering into this innovative technology. There are fundamentally three main types of 3D printers: Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), Stereolithography (SLA), and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS). Each type has its unique processes and benefits, making it crucial to choose the right one based on your specific needs and projects. Let’s explore the diverse world of 3D printing and discover which type of printer suits you best.
Key Takeaways
- Three Main Types: The three main types of 3D printers are Fusion Deposition Modeling (FDM), Stereolithography, and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS).
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): Popular desktop printing method for operational prototypes and ready-to-use products like LEGO bricks and plastic gears, using engineering-grade thermoplastics.
- Stereolithography (SLA) & Digital Light Processing (DLP): SLA uses UV-laser beams on liquid resin, producing smooth surfaces, while DLP is the fastest method, using arc lamps to harden resin quickly for high-resolution models.
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): Utilizes powdered materials with a laser to create strong 3D objects without additional support structures, enabling a wide selection of material options like nylon, glass, ceramic, and metal.
Understanding the Basics of 3D Printing
3D Printer Types: FDM, SLA, and SLS
To research into the world of 3D printing, it’s vital to grasp the different types of 3D printers available. With a focus on FDM, SLA, and SLS technologies, understanding the nuances of each is key to selecting the right tool for your needs. This means considering factors such as operational prototypes, material options, and production possibilities.
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
This type constructs 3D objects layer by layer using thermoplastic filament, ideal for mechanical engineers and manufacturers.

Stereolithography (SLA)
Offers smooth surfaces through the exposure of liquid resin to a UV-laser beam, requiring post-print processing for completion.
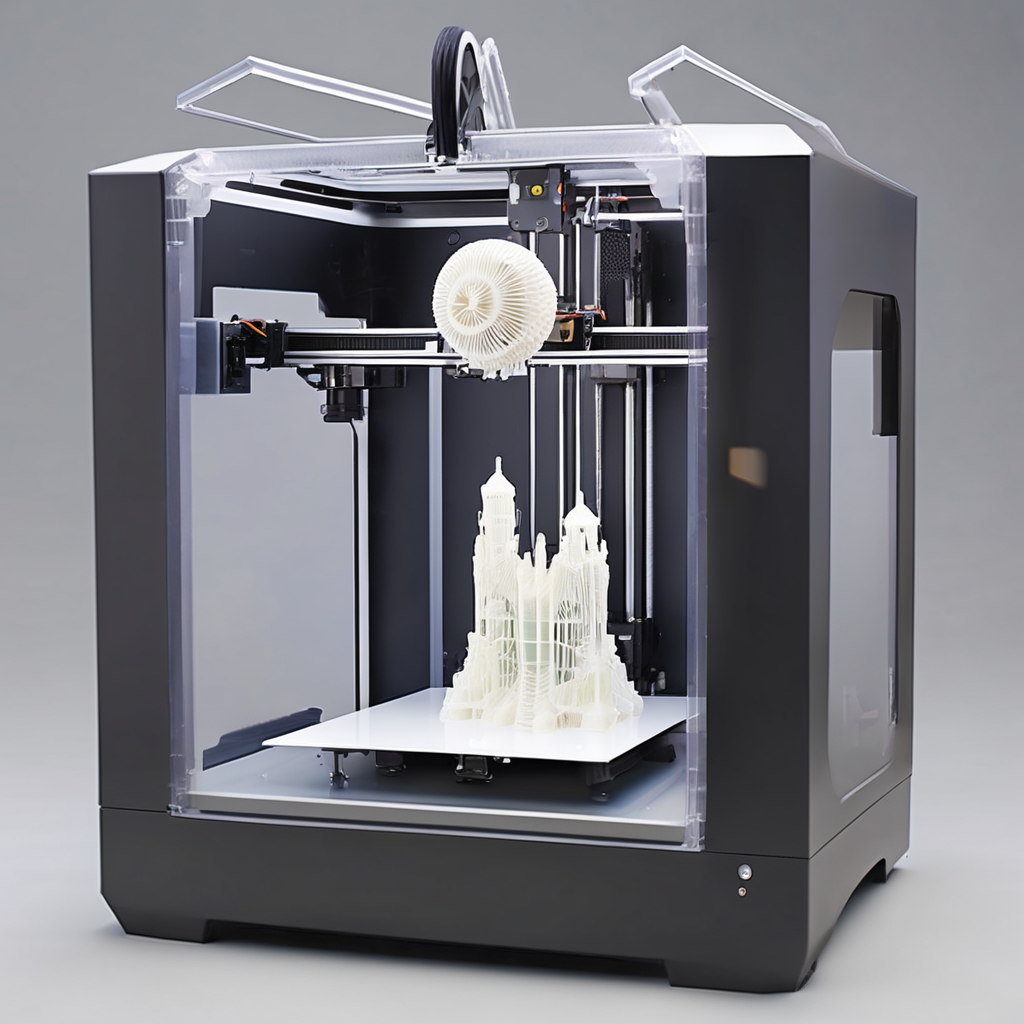
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
Uses powdered material and laser to create strong 3D printed objects, allowing for a wide range of material choices.

3D Printing Materials: PLA, PVA, and ABS
Materials play a crucial role in 3D printing. With a focus on PLA, PVA, and ABS, understanding the properties and applications of these materials is fundamental. PLA offers eco-friendly printing, ABS is suitable for connecting components, while PVA is ideal for dissolving in water. Making the right material choice is vital for achieving desired print quality and functionality.
What Should I Know Before Buying a 3D Printer?
Clearly, before purchasing a 3D printer, it is crucial to understand the basics such as the different types of 3D printers available, the materials they use, the process of printing objects, and the quality of output they offer. Conducting thorough research on these aspects will help you make an informed decision when selecting the right 3D printer for your needs.
3D Printer Filament Types
- Types of filaments
- Plastics
- Metals
- Ceramics
- Carbon Fiber
- Food products (e.g., chocolate)
After exploring the filament types, it’s important to choose the one that aligns with your specific 3D printing requirements.
Printing an Object: STL Files and Slicing Software
Types of 3D printing materials play a crucial role in determining the quality and durability of your printed objects. Understanding the various filament types such as plastics, metals, ceramics, carbon fiber, and even food products can help you make an informed decision when choosing a 3D printer.
Files: When printing a 3D object, utilizing STL files and slicing software is imperative. These files provide the specifications needed by the printer to create your desired object. Slicing software guides the printer on how to slice the object effectively, ensuring a precise and accurate print.
What is the Best 3D Printer for Beginners?
Kit Assembly and Material Considerations
Unlike more advanced users, beginners should opt for 3D printers that are pre-assembled or require minimal assembly. When considering material, beginners should lean towards PLA for ease of use and durability. PLA is a good material for beginners as it offers minimal shrinkage and warping.
Recommended 3D Printers for Beginners
What are the best 3D printers for beginners? For those starting out, machines like the MakerBot Replicator+ and the FlashForge Finder are excellent options. These printers offer high-quality 3D printing while being beginner-friendly and affordable.
A popular option for beginners is the FlashForge Finder, which provides an accessible printer at a reasonable price. The MakerBot Replicator+ is also highly recommended for its quality output and ease of use. These printers will help newcomers explore the world of 3D printing with confidence.
What are the Advantages of Owning a 3D Printer?
Lower Costs and Faster Development
Advantages of owning a 3D printer include lower costs and faster development. For those looking to build models for educational purposes, create displays, or build prototypes, 3D printing allows for cost-effective production at a faster rate. Medical teachers, for example, are able to create 3D models in a few hours rather than waiting for a delivery.
Prototyping and Manufacturing Efficiency
On a larger scale, owning a 3D printer also provides advantages in prototyping and manufacturing efficiency. Users can quickly prototype products, streamlining the development process and enabling faster iterations. For businesses, this means getting products to market more efficiently and with greater cost control. It also allows for increased customization and quick adjustments based on feedback.
What are the Pros and Cons of 3D Printing?
| Benefits | Drawbacks |
| Speed: 3D printing is more than 10 times faster than other methods, allowing rapid prototyping in hours. | Quality: Objects may not have the same finish as high-end prototyping machines, affecting overall quality. |
| Cost: Printing is five times cheaper, enabling cost-effective model creation and rapid product development. | Materials: Limited choices may impact the variety and quality of objects that can be printed. |
| Ease of Use: 3D printers are small, safe, reliable, and easy-to-use, making them popular outside of manufacturing. | Maintenance: In-house operations mean responsibility for repairs and correct materials, requiring trained personnel. |
Benefits: Speed, Cost, and Ease of Use
The speed and cost-effectiveness of 3D printing make it a valuable tool for rapid prototyping and product development. The ease of use and accessibility of 3D printers also contribute to their popularity.
Drawbacks: Quality, Materials, and Maintenance
While 3D printing offers speed and cost benefits, there are drawbacks to consider. The quality of printed objects may not match that of high-end machines, and limited material choices can impact the variety of objects that can be produced. Additionally, in-house maintenance and material considerations add to the overall complexity of utilizing 3D printing technology.
Other Types of 3D Printing Materials
Now, let’s explore the various materials that can be used in 3D printing. Understanding the different types of materials available for 3D printing is crucial in achieving your desired outcome. After all, the material used can greatly impact the final product.
| Plastics | Resin |
| Metals | Ceramics |
| Carbon Fiber |
Plastics, Resin, Metals, Ceramics, and Carbon Fiber
Other than the standard materials like plastics and metals, 3D printers can also work with materials such as ceramics and carbon fiber. Each material offers unique properties and characteristics, allowing for a diverse range of applications in 3D printing.
Food Products and Other Unique Materials
Other unique materials that can be used in 3D printing include food products like chocolate. This innovation allows for culinary creativity and personalized food creations like never before. The ability to 3D print with food opens up a whole new world of possibilities in the culinary arts.
The Best Questions to Ask for Choosing a Beginner 3D Printer
Budget and “Plug-and-Play” Considerations
Questions about budget and ease of use are crucial when selecting a beginner 3D printer. Keep in mind your financial limit and whether you prefer a “plug-and-play” device that requires minimal assembly. Consider if the printer will be solely for hobby use or if you plan to use it for business purposes as well.
Material Support and Feature Priorities
When choosing a beginner 3D printer, it’s imperative to think about the materials you need the printer to handle and the features that matter most to you. Consider whether the printer supports the materials required for your projects and prioritize features such as operation sound, connectivity options, and the printer size.
Understanding what materials your projects will require and prioritizing the features important to you can help you choose the best beginner 3D printer for your specific needs. By considering the materials the printer can support and the features it offers, you can ensure that the printer aligns with your project requirements and printing preferences, making your 3D printing experience more successful and satisfying.
Other Questions to Ask Yourself When Choosing a 3D Printer
Once again, when choosing a 3D printer, there are key questions you need to ask yourself to ensure you make the right decision. These questions will help guide you in finding the best 3D printer for your specific needs and requirements.
Budget and Material Considerations
Other than personal preferences, budget and material considerations play a crucial role in selecting a 3D printer. Determine how much your organization can invest and what type of materials you plan to use for your 3D printing projects. Understanding your budget and material requirements can help narrow down the options and ensure you choose a printer that suits your financial constraints and material needs.
Intended Product and Specialized 3D Printers
Printer, when selecting a 3D printer, take into account the intended products you will be printing. Different printers specialize in various types of objects and materials. Knowing the specifics of your printing goals can help you identify a printer that caters to your specific requirements, such as functional prototypes, custom parts, or intricate designs that may demand special materials.
To further enhance your understanding of specialized 3D printers, consider factors such as desired product quality, resolution, and material compatibility. By aligning your printing goals with the capabilities of specialized 3D printers, you can make a well-informed decision when choosing the best printer for your unique projects.
A Deep-Dive into 3D Printer Types
After discussing the basics of 3D printing, it’s time to investigate deeper into the different types of 3D printers available in the market. Each type of 3D printer offers unique features and advantages catering to various needs and requirements. This detailed breakdown will help you understand the capabilities and applications of each type of 3D printer.
| Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) | Stereolithography (SLA) |
| Digital Light Processing (DLP) | Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) |
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
Any discussion on 3D printer types would be incomplete without mentioning Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM). This popular method involves constructing 3D objects layer by layer using thermoplastic filament. FDM printers are known for their mechanical strength and heat resistance, making them ideal for a wide range of applications, from prototyping to end-product manufacturing.
Stereolithography (SLA)
DeepDive into Stereolithography (SLA) reveals a method using UV-laser beams to harden photosensitive liquid resin layer by layer into desired patterns. SLA 3D printers are favored for their ability to create smooth surfaces, although curing and finishing processes may vary. Despite longer processing times, SLA technology delivers high-resolution models efficiently.
Digital Light Processing (DLP)
Modeling in Digital Light Processing (DLP) involves using liquid resin melted by arc lamps to create 3D objects rapidly. This method offers impressive printing speeds due to quick resin hardening facilitated by a large amount of light. DLP printers are known for producing high-resolution models consistently, allowing for the use of various affordable materials.
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
Types of 3D printers like Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) utilize powdered material and a laser to create robust 3D objects without needing support structures. SLS technology offers a wide array of material options, including nylon, glass, ceramic, and metals, making it a popular choice for custom and intricate designs. To explore the full potential of SLS, understanding your material requirements is crucial.
Popular 3D Printer Options
High-Quality and Ease of Use: MakerBot Replicator+
Not all 3D printers offer the combination of high-quality printing and user-friendly experience quite like the MakerBot Replicator+. This 3D printer is a top choice for both beginners and experienced creators looking for consistent and reliable results with ease of use.
Beginner-Friendly and Affordable: FlashForge Finder
To cater to first-time 3D printers, the FlashForge Finder is a popular and accessible option at an affordable price point. Its user-friendly design and affordability make it a great choice for beginners looking to explore the world of 3D printing without breaking the bank.
Finder offers easy setup straight out of the box, making it an ideal choice for those eager to probe 3D printing without the hassle of complicated assembly. With its accessible price and beginner-friendly features, the FlashForge Finder is a popular choice for those new to the world of 3D printing.
Plug-and-Print: FlashForge Inventor II
Options like the FlashForge Inventor II are designed for those who want to start printing right away with minimal setup. The plug-and-print functionality of this 3D printer allows users to quickly get started with their printing projects without the need for extensive configuration or assembly.
For instance, the FlashForge Inventor II offers a seamless printing experience, perfect for those who value simplicity and convenience in their 3D printing endeavors. Its ease of use and plug-and-play functionality make it a popular choice for users looking for a straightforward printing solution.
Final Words
Drawing together the information presented, we have learned about four main types of 3D printers: Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), Stereolithography, Digital Light Processing (DLP), and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS). Each type offers unique features and benefits for different printing needs. By understanding the basics of these 3D printer types, individuals can make informed decisions when choosing the best printer for their specific requirements.
FAQ
Q: How many types of 3D printers are there?
A: There are three main types of 3D printers: Fusion Deposition Modeling (FDM), Stereolithography, and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS).
Q: What is Fusion Deposition Modeling (FDM)?
A: FDM is the most popular form of desktop 3D printing where components are printed layer by layer using thermoplastic filament.
Q: Explain Stereolithography (SLA) in 3D printing.
A: SLA involves exposing a layer of photosensitive liquid resin to a UV-laser beam to harden it in the desired pattern, building objects layer by layer.
Q: What is Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) technology?
A: SLS technology uses powdered material instead of liquid resin and a laser to form strong 3D printed objects without additional support structures.
Q: Can you elaborate on Digital Light Processing (DLP) in 3D printing?
A: DLP is a fast 3D printing method where liquid plastic resin is solidified using arc lamps, allowing for high-speed and high-resolution printing of complex objects.

